ASMART objectives are an essential aspect of personal and professional development. It provides a structured approach ensuring that objectives are Aligned, Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. By adhering to these six principles, employees and organisations can increase their likelihood of success and enhance their overall productivity.
Table of Contents
Goals versus Objectives
A goal is a desired state/outcome that is generally broad and is long term. A goal gives direction, purpose and may encompass multiple objectives.
An objective is specific, short term and defines measurable actions to achieve an overall goal, allowing progress to be tracked and evaluated.
In summary goals provide the overarching vision or direction, while objectives are the specific, measurable steps taken to realise that vision. Objectives serve as the building blocks for achieving the goals, supporting to focus efforts and monitor progress along the way.
What Are ASMART Objectives
The main objective of ASMART is to start thinking about areas that need improvement.
ASMART is an acronym and stands for Aligned, Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-bound. The ASMART objectives provide the details, based on these six principles, for how the employee or organisation will achieve their goal.
- Aligned: Aligned with company / team goals and priorities
- Specific: Should be well-defined and unambiguous
- Measurable: Can be quantified or qualified at the end of the year
- Attainable: Should be realistic and achievable
- Relevant: Consistent with achieving company goals and objectives
- Time-bound: Indicate timeframe or target date for completion
How to Write Good ASMART Objectives
Writing good objectives involves following the ASMART criteria:
Step 1. Aligned
Make sure that what you want to achieve is linked to the team goals, priorities and the company’s strategy, and/or values.
Step 2. Specific
Clearly define what you want to achieve. Your objective should be well-defined and focused, answering questions like who, what, where, when, and why. Specific should not be interpreted as: “long”, “a lot of text”, “minor details”, or a “task list”.
Step 3. Measurable
Establish concrete criteria for measuring progress and success. Define how you will track your progress and determine when the objective has been achieved.
Step 4. Attainable
Ensure that your objective is realistic and attainable. Consider the resources, skills, and time available to you, and set goals that you have the ability to accomplish.
Step 5. Relevant
Align your objective with your broader goals and objectives. It should be relevant to your overall mission and contribute to your long-term success.
Step 6. Time-bound
Set a deadline or timeframe for achieving your objective. This creates a sense of urgency and helps you stay focused on making progress within a specific timeframe.
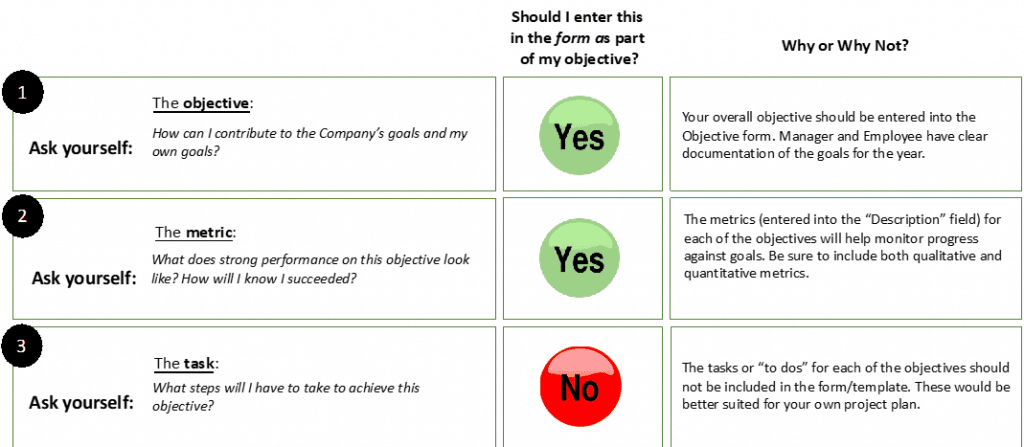
The Metric
Metrics should be written as an outcome of the work, not the work itself.
Example: “Make 10 sales calls” is a task, “exceed sales targets” is a metric.
Metrics should not be a listing of tasks or project steps and should be limited to the key outcomes for the year.
In summary, learning how to set ASMART objectives can help companies, employees and managers reach their targets more efficiently.
By applying these criteria, you can write ASMART objectives that are aligned, clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, setting yourself up for success in reaching your goals.
Performance Management
Performance management can improve employee engagement and thus support employees becoming more productive, develop new skills and actively participate in advancing organisational goals.
The Performance Management Strategy is the integrated approach to achieving goals by monitoring and improving the performance of people, teams, and the organisation as a whole.
The Performance Management cycle throughout the year connects individual objectives, behaviours and performance to the evolving company objectives and HR Strategy. Performance at the company thrives when managers engage in frequent coaching conversations with employees.
Objective Setting Conversation
- The objective setting conversation takes place in the beginning of each year and are part of the Performance Management cycle of a company.
- It provides the foundation for performance feedback and development throughout the year.
- The performance ASMART objectives tie in to the company’s goals and the company behaviours.
- It enables selection of clear, measurable activities that drives employee performance.
- The conversation provides dialogue, coaching, and feedback opportunities between manager and employees.
Responsibility Managers and Employees During the Objective Setting Conversation
Manager
- Provides clear, actionable feedback and coaching regarding the objectives.
- Helps employees identify the areas of focus in order to align with corporate goals.
- Leverages an employee’s strengths and interests when goal setting.
- Discusses the objectives and goals during regular 1:1 meetings and measures progress.
- Works with employees to find the right solutions related to work/life considerations.
- Articulates linkage between work and projects that tie to the company mission and goals.
Employee
- Incorporates feedback regarding objectives and work actions for the metrics.
- Matches the identified areas of focus of corporate goals and includes them as part of the objective.
- Utilises the strengths and infuses them into the work to achieve corporate goals.
- Discusses with the manager objectives and goals during regular 1:1 meetings and measures progress.
- Recognises and understands the linkage between work and projects that tie into the company mission and goals.